Augmented Reality Blending the Real and Digital
Augmented Reality Blending the Real and Digital
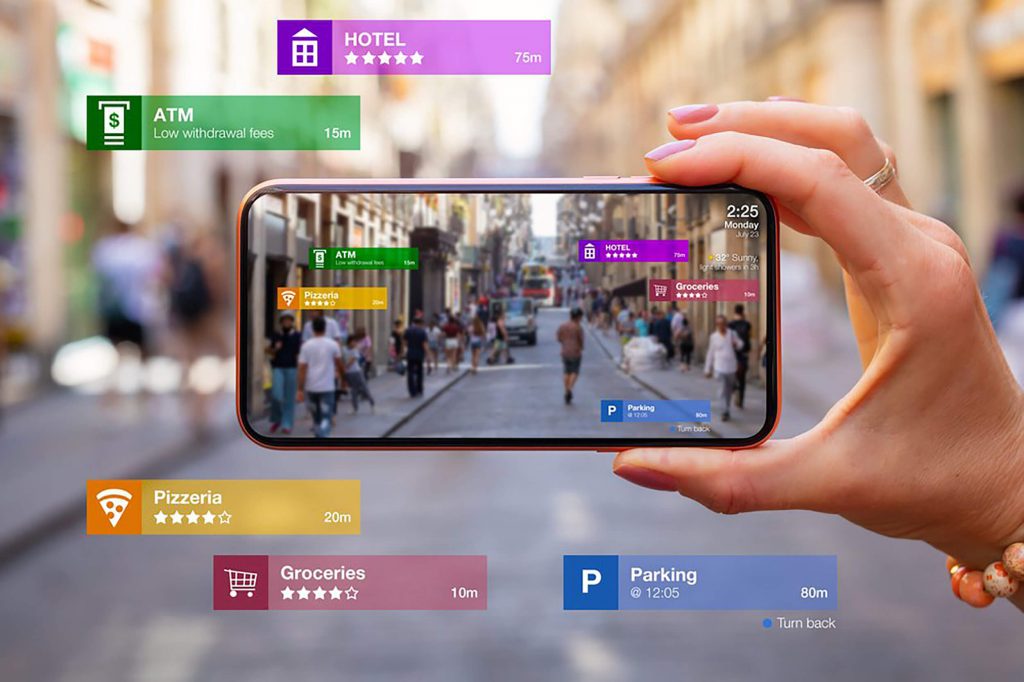
Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that overlays digital information on top of the real world, enhancing our perception of reality. It uses devices like smartphones, tablets, and headsets to create an interactive experience.
How AR Works
- Camera: A device’s camera captures a real-world scene.
- Sensors: Sensors in the device track the user’s position and orientation.
- Digital Content: Digital content, such as images, text, or 3D models, is generated and superimposed onto the real-world scene.
AR Applications
- Gaming: AR games like Pokémon Go have become popular, allowing players to interact with digital creatures in the real world.
- Education: AR can provide interactive learning experiences, such as virtual field trips or anatomy lessons.
- Retail: AR can be used for virtual try-ons, allowing customers to see how products would look on them.
- Manufacturing: AR can be used for assembly instructions, maintenance, and quality control.
- Architecture and Design: AR can be used to visualize building designs and make changes before construction.
Challenges and Future of AR
- Hardware Limitations: Current AR devices may have limitations in terms of processing power, battery life, and display quality.
- Content Creation: Creating high-quality AR content can be time-consuming and expensive.
- User Experience: Ensuring a seamless and comfortable AR experience can be challenging.
Despite these challenges, AR has the potential to transform many industries and enhance our daily lives. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative and immersive AR applications.



